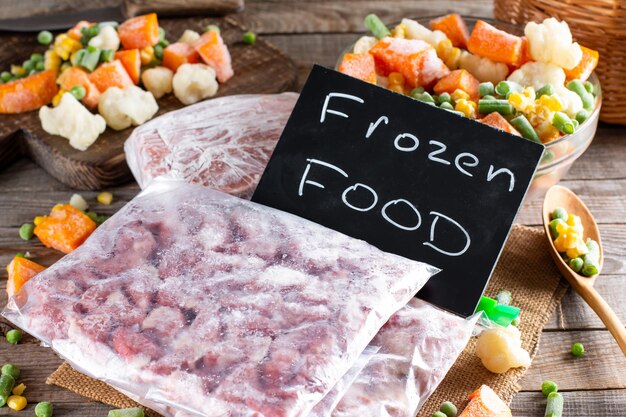
As modern lifestyles become increasingly busy, consumers are paying closer attention to how food choices impact health and convenience. One of the most common debates in everyday nutrition is whether frozen food is as nutritious as fresh food. While fresh food is often perceived as the healthier option, advances in food preservation have changed the nutritional landscape. Understanding how frozen and fresh foods compare nutritionally can help consumers make informed decisions based on facts rather than assumptions.
How Freezing Affects Nutrients
Freezing is one of the most effective methods for preserving food. The process slows down enzymatic activity and microbial growth, both of which cause food to spoil and lose nutritional value. Most foods are frozen shortly after harvesting or preparation, which helps lock in vitamins, minerals, and natural flavors.
Although some nutrients, such as vitamin C, may experience slight losses during initial processing, the overall nutritional profile of frozen food remains largely intact. In many cases, frozen food retains its nutrients better than fresh food that has been stored for several days.
Fresh Food and Nutrient Loss Over Time
Fresh food is often associated with superior quality and nutrition, but this depends largely on how it is handled. From the time fresh food is harvested, nutrients begin to degrade due to exposure to air, light, and temperature changes. Transportation, storage, and prolonged shelf time can further reduce nutrient levels.
For consumers who do not consume fresh food immediately, the nutritional difference between fresh and frozen options may be smaller than expected. In some cases, frozen food can even offer a more stable nutrient profile over time.
Comparing Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are essential components of a healthy diet. Studies comparing frozen and fresh foods show that levels of key nutrients such as iron, calcium, and protein remain comparable in both forms. Fat-soluble vitamins are generally stable during freezing, while water-soluble vitamins may see minor reductions.
The key factor is not whether food is frozen or fresh, but how it is processed and stored. Proper freezing techniques help preserve nutritional value, making frozen food a reliable alternative for maintaining dietary balance.
Role of Processing and Preparation
It is important to differentiate between minimally processed frozen foods and heavily processed frozen meals. Simple frozen items, such as meats or vegetables, typically retain most of their nutritional benefits. On the other hand, frozen foods with added sugars, sodium, or unhealthy fats may offer lower nutritional value.
Consumers should read labels carefully to choose frozen products with fewer additives. Brands like Orange Food Expert focus on maintaining quality standards and offering frozen products that align with nutritional expectations, supporting healthier food choices.
Food Safety and Nutritional Stability
Food safety plays a significant role in nutrition. Frozen food benefits from reduced bacterial activity, which helps maintain both safety and quality. When food remains safe for consumption, its nutritional value is also better preserved.
Fresh food that is improperly stored or kept for too long may not only lose nutrients but also pose safety risks. Frozen food, when handled correctly, provides a consistent and dependable option.
Impact on Dietary Planning
Frozen food supports better meal planning by offering long-term storage and portion control. This allows consumers to plan balanced meals without the pressure of immediate consumption. By reducing food waste, frozen food also helps ensure that nutritional resources are used efficiently.
For busy households, frozen food offers the flexibility to maintain nutritional intake without daily grocery shopping. This practicality makes it easier to follow consistent eating habits.
Misconceptions About Taste and Quality
Many people believe that frozen food lacks the taste or texture of fresh food. However, modern freezing technology has significantly improved sensory quality. Quick-freezing methods preserve texture, color, and flavor, resulting in products that closely resemble fresh food when prepared properly.
This improvement in quality has contributed to increased acceptance of frozen food as a regular dietary option.
Conclusion
The nutritional difference between frozen and fresh food is often smaller than commonly believed. While fresh food can be highly nutritious when consumed immediately, frozen food offers comparable nutritional value with added benefits of longer shelf life, reduced waste, and consistent quality. By choosing quality-focused options from trusted brands like Orange Food Expert, consumers can confidently include Frozen Food Items in their diets as a practical and nutritious alternative to fresh foods in today’s fast-paced world.