Copper mining is the process of extracting copper metal from its ores, which typically contain less than 1% copper. It involves various methods, including open-pit and underground mining, depending on the location and geology of the deposit. The end goal is to produce high-purity copper cathodes that serve as raw material for countless industrial and technological applications.
The process requires complex techniques tailored to the type of ore, primarily copper oxide or copper sulfide, using hydrometallurgy or pyrometallurgy, respectively. Copper plays a critical role in sectors such as electrical infrastructure, renewable energy, and transportation due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Global copper production is dominated by countries like Chile, with Canada also ranking high in output. Increasing demand fueled by the transition to green energy is driving the expansion and modernization of copper mining operations worldwide.
Copper Mining Processes
Copper mining involves several precise steps from locating deposits to extracting and processing ore while managing environmental impact. Each stage requires specialized techniques to efficiently convert raw materials into usable metal.
Exploration and Discovery
Exploration begins with geological surveys to identify copper-rich areas, often using remote sensing and geophysical methods. Once promising sites are found, drilling samples helps determine ore quality and quantity.
Detailed mapping and sampling continue to assess mineral distribution and depth. This phase is crucial for planning the mining approach and estimating project feasibility.
Exploration efforts can take years and involve both surface and subsurface investigations. Accurate data reduces risks and guides investment decisions before extraction begins.
Extraction Methods
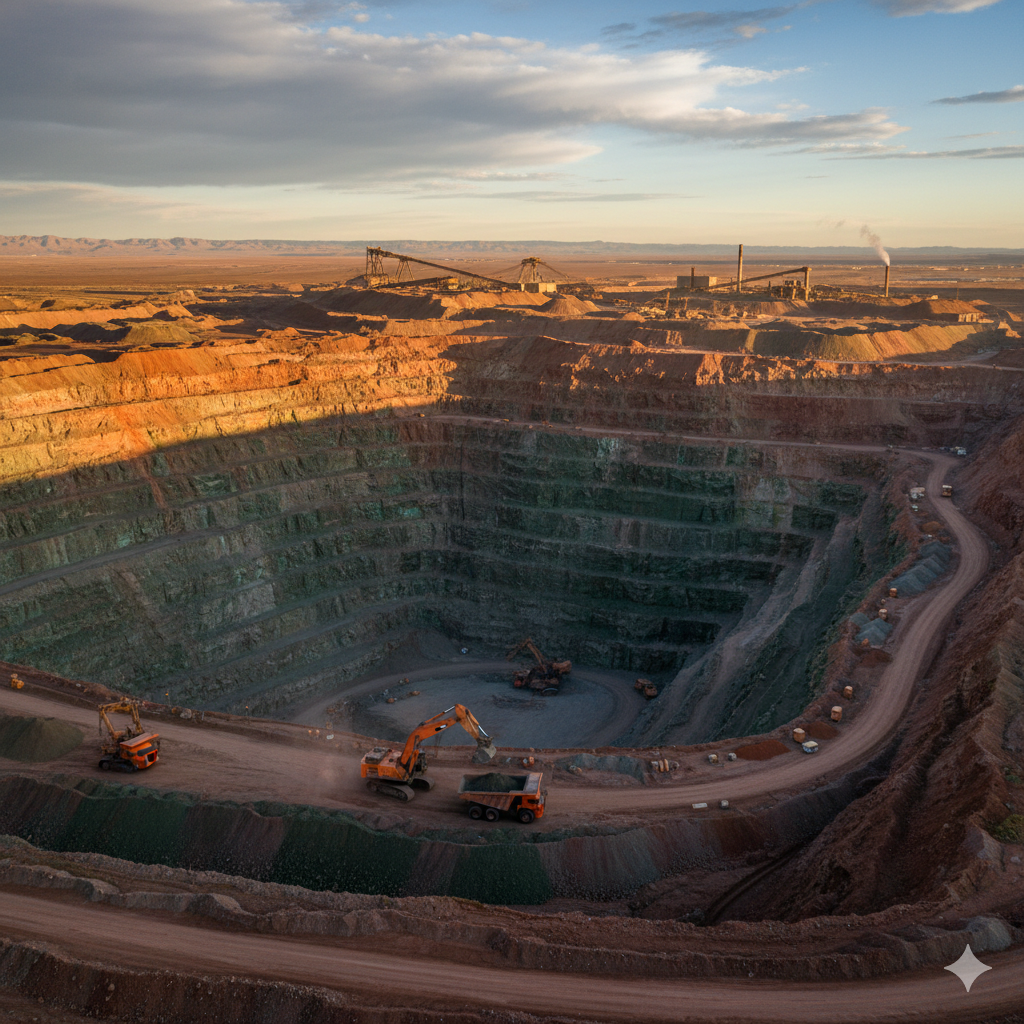
Copper extraction depends largely on the ore type and deposit location. The two primary methods are open-pit mining and underground mining.
Open-pit mining exposes large ore bodies near the surface. It involves removing overburden, blasting, and hauling ore for processing.
Underground mining targets deeper deposits. Miners create tunnels or shafts to access ore, which is then brought to the surface.
Each method demands careful consideration of economic, technical, and safety factors to optimize recovery and minimize costs.
Ore Processing
Processing copper ore transforms raw material into pure metal. Ores such as copper oxide and copper sulfide require different techniques.
Copper oxide is typically treated by hydrometallurgy, involving crushing, grinding, and leaching to extract copper ions. This process improves recovery rates from low-grade ores.
Copper sulfide ores undergo pyrometallurgy, which includes concentrating, smelting, and refining. The ore is first concentrated by flotation, then smelted to remove impurities before refining into cathodes with purity around 99.99%.
Each step combines physical and chemical processes tailored to the specific mineralogical characteristics.
Environmental Management
Copper mining operations implement measures to reduce environmental impact. This includes managing waste rock and tailings to prevent contamination.
Water treatment systems are crucial to control acid mine drainage and protect local ecosystems. Reclamation plans restore mined land after operations finish.
Regulatory compliance drives continuous monitoring of air and water quality. Sustainable practices also focus on energy efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
These controls are integral to responsible mining, balancing production with environmental stewardship.
Economic and Industrial Significance
Copper mining remains a critical component of the global economy and industrial development due to its extensive use, widespread production, and regional importance. Its role spans from raw material extraction to advanced industrial applications, influencing trade, infrastructure, and technological progress.
Global Copper Production
Chile leads global copper production, contributing approximately 27% of the world’s output. Large mines such as Escondida and Collahuasi drive this dominance, maintaining copper supply stability for international markets.
Other significant producers include Peru, China, and the United States. The industry’s scale and efficiency have improved with better mining technology and processing methods, catering to rising demand, especially from green energy sectors.
Copper production is also linked to economic growth in producing countries, supporting jobs, public services, and infrastructure projects through mine revenues.
Major Copper Mining Regions
Key copper mining regions are concentrated in South America, North America, and parts of Asia.
South America hosts the most productive mines, with Chile and Peru as leading nations. Collahuasi in Chile is noted for high-grade, long-life reserves, crucial for predictable supply chains.
North America’s Ring of Fire in Canada is emerging for its potential in large-scale copper operations, supporting the nation’s green economy transition.
Asia’s contribution focuses on processing and refining, often complementing raw extraction from other regions by adding value to the copper supply chain through manufacturing and trade policies.
Applications in Industry
Copper’s excellent electrical conductivity makes it indispensable in wiring and electrical infrastructure.
Its resistance to corrosion and malleability are valuable in plumbing, industrial machinery, and construction.
Copper is essential in emerging clean technologies such as solar panels, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems, linking it directly to the global energy transition.
Industries also utilize copper in manufacturing electronic devices and transportation equipment, making it a foundational metal in modern industrial economies.