Digestive health plays a critical role in overall well-being, as the digestive system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. Digestive health disorders occur when this complex system is disrupted, leading to discomfort, nutritional deficiencies, and reduced quality of life. These conditions range from mild and temporary issues to chronic diseases requiring long-term medical care.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and medical management of digestive disorders is essential for early diagnosis, effective treatment, and prevention of complications.
Understanding Digestive Health Disorders
Digestive health disorders affect the gastrointestinal tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. When any part of this system fails to function properly, it can result in symptoms that interfere with daily activities and overall health.
Common digestive disorders include acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastritis, constipation, diarrhea, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and liver-related conditions. These disorders may be acute or chronic and often require a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatment.
Common Causes of Digestive Disorders
Digestive health disorders can develop due to multiple factors, including lifestyle habits, medical conditions, and environmental influences.
Poor Dietary Habits
Diets high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, and low fiber can disrupt digestion and lead to bloating, constipation, and inflammation. Inadequate hydration also affects bowel regularity.
Chronic Stress
Stress affects gut motility and enzyme secretion, often worsening symptoms like abdominal pain, indigestion, and irregular bowel movements. The gut-brain connection plays a significant role in digestive health.
Infections and Inflammation
Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can inflame the digestive tract, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and food intolerances can negatively affect digestion and nutrient absorption.
Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, including antibiotics, pain relievers, and some chronic treatments, may disrupt gut balance or irritate the stomach lining.
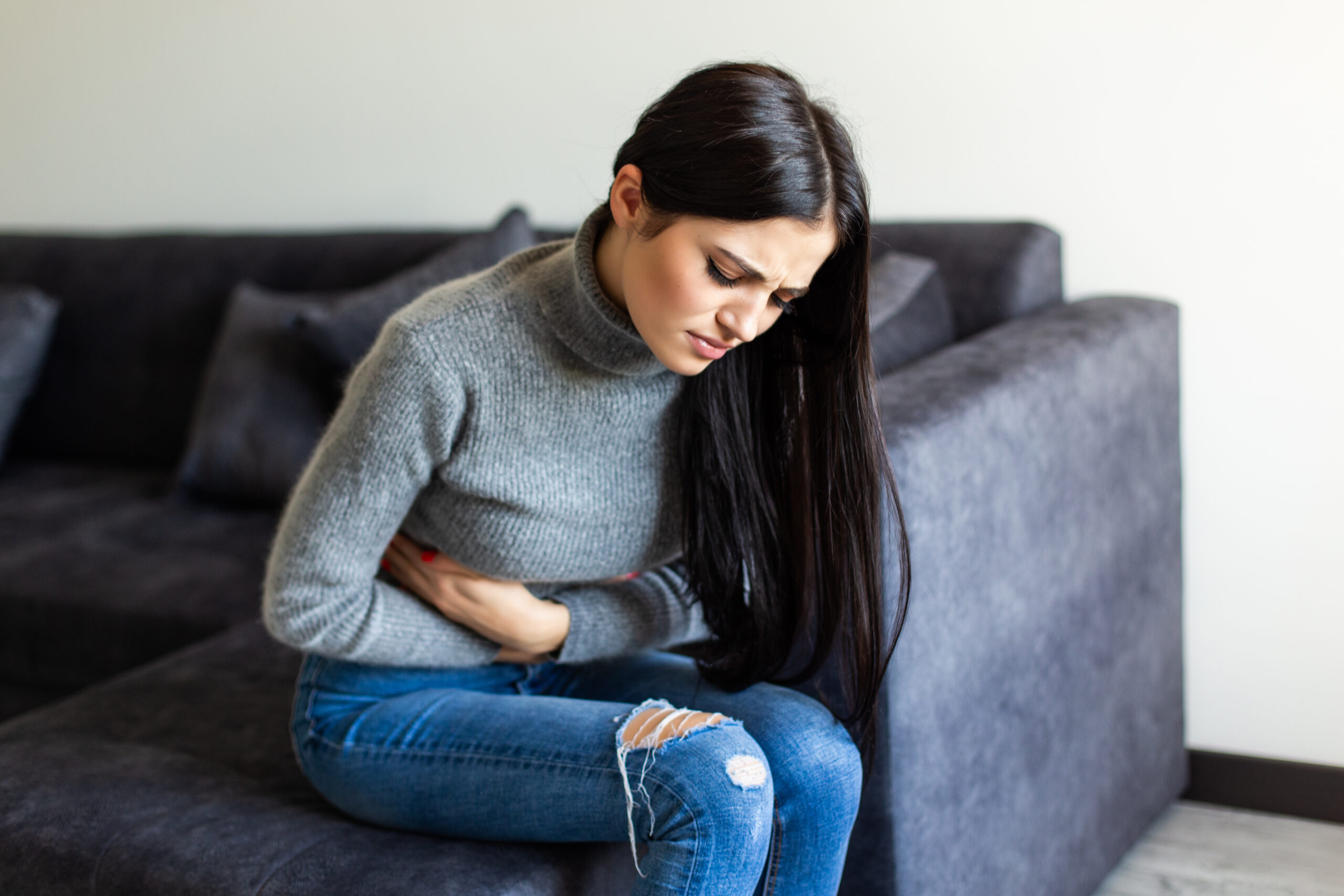
Symptoms of Digestive Health Disorders
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the disorder. Common signs include:
-
Abdominal pain or cramping
-
Bloating and excessive gas
-
Heartburn or acid reflux
-
Constipation or diarrhea
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Changes in appetite
Persistent or severe symptoms should never be ignored, as they may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Diagnosis and Clinical Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management of digestive disorders. Healthcare providers use a combination of clinical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
-
Blood tests to detect inflammation or infections
-
Stool tests to evaluate digestive function
-
Endoscopy or colonoscopy for visual examination
-
Imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans
Early diagnosis allows timely intervention and reduces the risk of complications.
Medical Management of Digestive Disorders
Treatment depends on the specific disorder and its underlying cause. Medical management may include:
Medications
Doctors may prescribe antacids, proton pump inhibitors, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, or enzyme supplements to control symptoms and treat the root cause.
Dietary Modifications
Patients are often advised to adopt a balanced, fiber-rich diet, avoid trigger foods, and maintain regular meal schedules to support digestive function.
Stress Management
Since stress significantly affects digestion, relaxation techniques, counseling, and lifestyle adjustments are often part of treatment plans.
Probiotics and Supplements
In some cases, probiotics or nutritional supplements may be recommended to restore gut balance and improve digestion.
Reliable platforms like Medslike provide educational information on digestive health medications, treatment options, and safe usage guidelines, helping individuals make informed healthcare decisions.
Preventive Strategies for Digestive Health
Preventive care plays an important role in maintaining digestive health and reducing the risk of disorders. Key strategies include:
-
Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber and nutrients
-
Staying hydrated throughout the day
-
Engaging in regular physical activity
-
Managing stress effectively
-
Avoiding excessive alcohol and smoking
-
Seeking medical advice for persistent symptoms
Adopting healthy habits early can significantly improve long-term digestive function.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Medical consultation is necessary if digestive symptoms persist, worsen, or interfere with daily life. Warning signs that require prompt evaluation include:
-
Severe or persistent abdominal pain
-
Blood in stool
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Chronic vomiting or diarrhea
-
Difficulty swallowing
Early intervention can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes.
Long-Term Outlook
With proper diagnosis and medical management, many digestive health disorders can be effectively controlled. Patients who follow treatment plans, adopt healthy lifestyle changes, and attend regular medical checkups often experience significant symptom improvement and better quality of life.
Digestive health disorders are common but manageable conditions that can significantly affect daily life if left untreated. Understanding their causes, recognizing symptoms early, and seeking appropriate medical management are essential steps toward maintaining digestive wellness. Through preventive care, lifestyle modifications, and reliable medical guidance from trusted sources like Medslike, individuals can support healthy digestion and long-term gastrointestinal health.