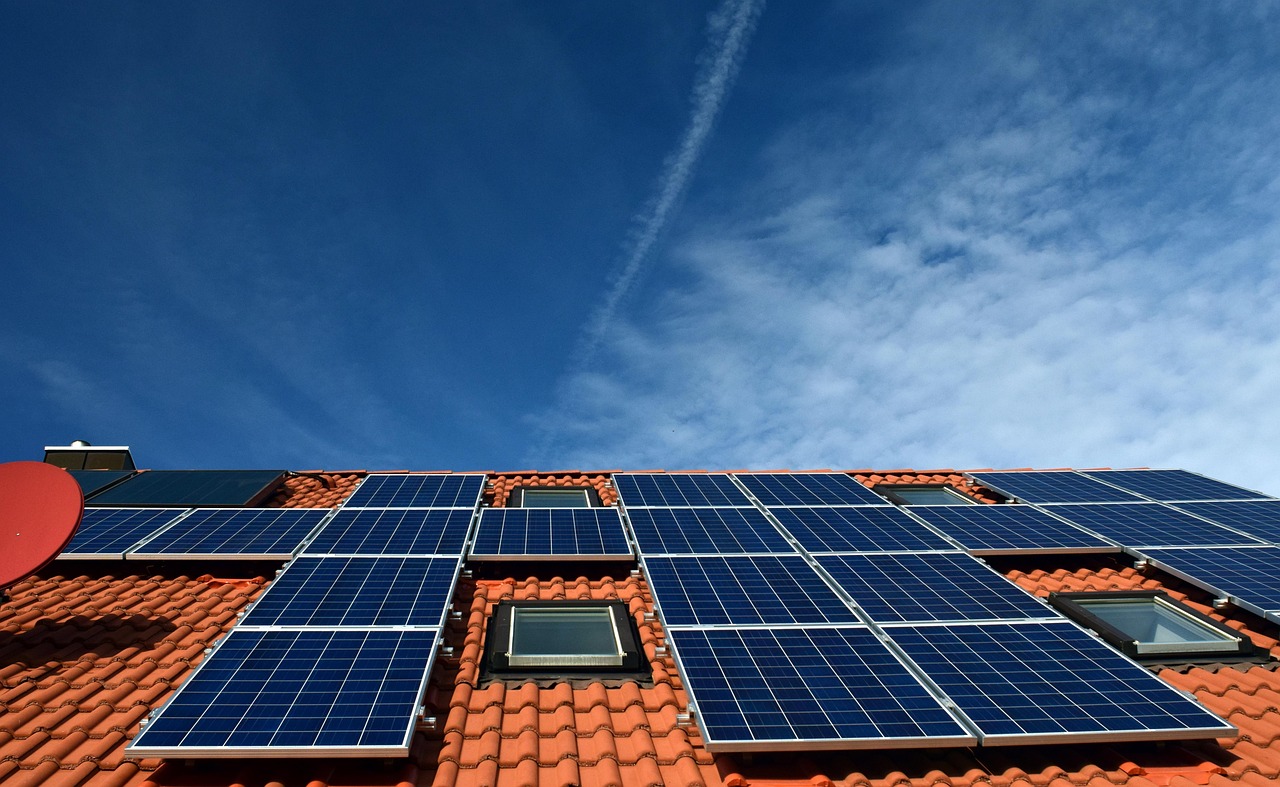
Solar glass panels are an innovative technology that integrates photovoltaic cells into transparent glass, allowing windows to generate electricity while maintaining visibility. They convert sunlight into usable energy without compromising the aesthetics or function of traditional glass surfaces. This makes them a practical solution for buildings aiming to combine sustainable energy with modern design.
These panels capture sunlight including ultraviolet and infrared light, converting it to power while letting visible light pass through. This technology is adaptable to various building types, from homes to skyscrapers, offering flexibility in architectural applications. With ongoing advancements, solar glass panels are becoming a key component in energy-efficient, sustainable construction.
Overview of Solar Glass Panels
The Solar glass panels combine transparent glass with photovoltaic technology to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. Their design varies to fit different building needs, with distinct types offering varying durability and efficiency. The functional process involves light transmission, energy conversion, and protection of internal solar cells.
What Are Solar Glass Panels?
Solar glass panels are photovoltaic modules where solar cells are laminated between layers of glass. They act as both a protective cover and an energy-harvesting surface. The glass used is typically low-iron to maximize light transmission and reduce color distortion, ensuring more sunlight reaches the cells.
These panels are built to withstand environmental stresses, like wind, rain, and temperature changes. Some versions include smart features that monitor performance and optimize energy output in real-time. Their transparency allows for integration into windows and building facades without blocking natural light.
Types of Solar Glass Panels
Two common types are glass-foil and glass-glass solar panels. Glass-foil panels have a glass front and a polymer backsheet, which is lighter but less durable. Glass-glass panels sandwich solar cells between two glass layers, enhancing durability and lifespan.
The glass-glass design offers better protection against moisture and mechanical damage, making it suitable for harsh environments. Meanwhile, glass-foil panels are usually lighter and less expensive, often preferred for residential installations. The choice depends on factors like cost, application, and environmental conditions.
How Solar Glass Panels Work
Solar glass panels work by allowing sunlight to pass through the glass to reach photovoltaic cells underneath. These cells convert light into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. The glass must be clear and low in iron to reduce light loss and improve energy efficiency.
After conversion, the energy is directed to an inverter that turns it into usable electricity for buildings. Advanced panels may include integrated energy storage or smart systems to store excess power or monitor performance in real-time. The glass layers simultaneously protect cells from weather and physical damage.
Applications and Benefits
Solar glass panels integrate renewable energy generation with building surfaces. They offer versatile uses across various settings and improve energy capture, durability, and aesthetics.
Residential Installations
Solar glass panels are increasingly popular in residential buildings. They function as windows or skylights that generate electricity while maintaining transparency.
Homeowners benefit from reduced reliance on the grid and lower energy costs. The integration into windows preserves natural light without compromising the home’s appearance.
These panels also provide durability and weather resistance, ensuring long-term performance and minimal maintenance. Many installations enhance property value by combining sustainability with modern design.
Commercial and Industrial Uses
In commercial and industrial settings, solar glass panels contribute to large-scale energy production. They are installed on facades, roofs, and skylights, enabling buildings to produce electricity on-site.
They support compliance with green building standards and reduce operational energy expenses. The panels’ transparency allows buildings to maintain natural lighting while producing power.
Their robust construction suits diverse environmental conditions common in industrial areas. Additionally, they help companies meet sustainability goals without altering architectural aesthetics.
Energy Efficiency Advantages
Solar glass panels improve energy efficiency by maximizing sunlight capture through dual glass layers or transparent photovoltaic cells. This design increases energy output compared to traditional opaque panels.
The glass protects solar cells from environmental damage, extending lifespan and reducing performance degradation. This results in consistent energy generation over decades.
These panels also add insulating properties, helping regulate indoor temperatures and decreasing heating or cooling demands. The combination of power generation and building insulation makes them valuable for sustainable energy strategies.
| Benefit | Description |
| Enhanced sunlight capture | Transparent solar cells increase efficiency |
| Durability | Glass shields cells from weather and damage |
| Dual function | Generate electricity while serving as windows |
| Energy savings | Reduces grid dependence and operational costs |